Realizing a Decarbonized Society
Basic policy
One of the most important social issues the world faces is climate change. The resulting increase in natural disasters, food-related problems, and droughts have become serious issues affecting even national security. Amid this, companies are being asked to intensify their mitigation and adaptation efforts with regard to climate change.
The AMADA Group’s Management Philosophy is to respect all stakeholders and the global environment, and in our Environmental Declaration, we strive to become a company that connects with customers, society, and the world through ecological manufacturing. Accordingly, realizing a decarbonized society is one of our material social issues. Respecting the scientific findings of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) and other organizations, as well as international agreements concerning the Paris Agreement, we are taking action to reduce our greenhouse gas emissions to achieve the relevant environmental goals from each of the above accords.
We have set respective reduction targets for Scope 1 and 2 emissions and for Scope 3 emissions for 2025 and 2030 (with consideration for 2040 and 2050). We are working as a Group to reduce emissions through energy-saving activities and the use of renewable energy for Scope 1 and 2, and, for Scope 3, by visualizing emissions in the supply chain and expanding the development and sales of Amada Eco Products.
For more information on the financial impact of climate change, please see the page linked below.
Product planning, development, and procurement
At the product planning, development, and procurement stages, we set clear goals for their environmental performance and conduct evaluations at each step of development in order to launch products with industry-leading environmental performance.
Product manufacturing
At the AMADA Group, to reduce CO₂ emissions from business sites and plants (Scope 1 and Scope 2), we have been reducing energy consumption through energy-saving measures such as use of power-saving lighting, upgrading to high-efficiency air conditioning equipment, and improving production efficiency in each process. In addition, with regard to renewable energy, we are moving forward with efforts to systematically introduce renewable energy and green electricity by expanding the scope of renewable energy use beyond the previous limited area in Japan and overseas.
Clean factories
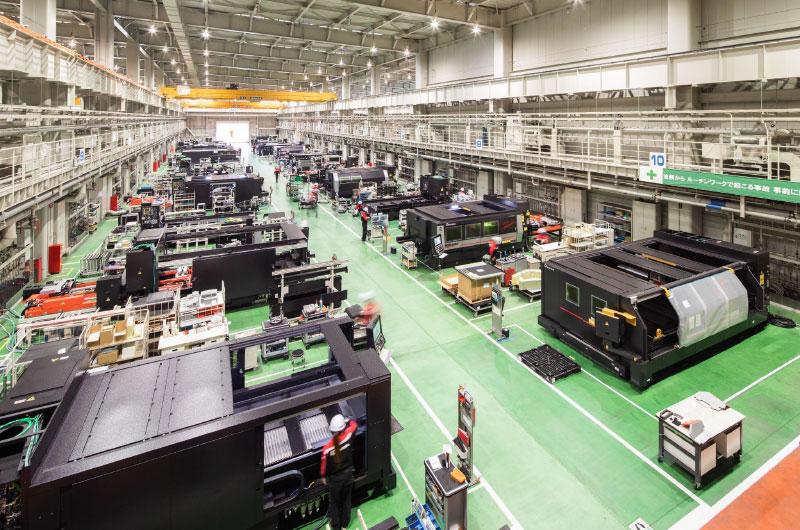

We also promote energy conservation and reduction of CO₂ emissions to mitigate global warming, as well as reduction of waste, and reduction of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) used in our factories. Environmentally friendly factories like these, which have reduced the environmental impact from their production activities, are called “clean factories” at AMADA. The Fourth Factory at the Fujinomiya Works is one of the world’s largest laser machine assembly plants, but it is also a plant that deserves to be called a clean factory.
Introduction of renewable energy

The AMADA Group promotes the use of renewable energy at its production sites. Solar panels have been installed in phases at seven of our Move to the next line business sites and plants in Japan, as part of our efforts to introduce renewable energy. In addition, in fiscal 2022 we procured non-fossil certificates for all electricity used at our sites in Japan, which will be derived from natural renewable energy sources. In effect, this means we have used 100% renewable energy for the fiscal year domestically.
As for our overseas locations, our Solution Center in Haan, Germany, has been using geothermal heat pumps since 2009. This facility covers 80% of the energy needed for air conditioning each year through 52 ground heat exchangers installed 130 meters underground, reducing CO₂ emissions by 40%. In addition, solar power generation systems have been installed at AMADA ITALIA S.r.l., AMADA LIANYUNGANG MACHINE TECH CO., LTD., AMADA AUTOMATION EUROPE, our subsidiaries in Italy, China, and France, respectively. In fiscal 2023, we joined RE100, an international environmental initiative that aims to source 100% renewable electricity for all business activities at all locations. The Group will continue to advance higher-quality renewable energy measures in addition to tireless energy conservation.
For our track record of renewable energy installations, please see the page linked below.
Example initiatives at individual sites
Isehara Works
Amada Global Innovation Center
Our existing Solution Center was completely overhauled to create the AMADA GLOBAL INNOVATION CENTER (AGIC), a base for innovation creation which opened in February 2023.
By introducing the latest air conditioning equipment and lighting to save energy and using renewable energy from solar power generation, AGIC has reduced CO₂ emissions by 700 tons per year compared to previous levels.

- Electric air-cooled heat pump chiller air conditioning system
- Our air conditioning system was upgraded from a conventional gas absorption chiller/heater system to a high-efficiency modular electric air-cooled heat pump chiller system (low global warming potential (GWP) modular chiller*).
By switching from gas to electricity and adopting an inverter pump with variable flow according to demand, CO₂ emissions will be reduced by 60% (126t-CO₂/year) compared to before the upgrade.- This system uses R32, a refrigerant with low GWP, approximately 68% lower than the conventional R410A refrigerant. As a result, global warming impact is significantly reduced.

- Solar power facilities for energy creation
- AGIC features solar panels with an installed capacity of 255 kW, capable of generating 220 MWh per year (10% of existing electricity usage) and thereby eliminating 100 tons of CO₂ emissions per year.
- Exhibition area sensing air conditioner
- Thanks to powered variable air volume (PVAV), this air conditioner functions with reduced fan power. This reduces CO₂ emissions by 20% versus the pre-upgrade level (-11 t-CO₂/year).
By installing wireless thermostats in the areas where people are and adjusting the outside air flow by sensing the number of people, we reduce CO₂ emissions by 6% (-6 t-CO₂/year) in relation to the heat load in the exhibition rooms.
AMADA TECHNICAL EDUCATION CENTER (ATEC)

AMADA TECHNICAL EDUCATION CENTER (ATEC) is a comprehensive training facility designed to be “a place to educate the next generation of engineers capable of envisioning the future of customer factories.” We opened in October 2024.
This facility is equipped with an electric air-cooled heat pump chiller air conditioning system similar to AGIC's, and also features solar panels with an installed capacity of 200 kW.
AMADA FORUM

- Upgrading to environmentally friendly equipment
- In 2022, our air conditioning system was replaced with a waste heat input gas absorption chiller/heater, and a high-efficiency modular electric air-cooled heat pump chiller system (low GWP modular chiller) and inverter-controlled variable flow pump were installed to meet the load.
In addition, a waste heat input hot water boiler was installed to provide both air conditioning (heating) and hot water supply.
Furthermore, with the micro-cogeneration* system, we reduce gas consumption by taking demand countermeasures and supplying waste heat (hot water) to the cold/hot water generator and boiler, respectively. These facility upgrades will reduce CO₂ emissions by 40% (-258 t-CO₂/year).
In addition, the use of R32—a refrigerant with low GWP, approximately 68% lower than the conventional R410A refrigerant—has significantly reduced the impact of the system on global warming.- In the event of a disaster (power outage), the micro-cogeneration system can be used to secure electric power (lights, outlets, networks, ventilation, etc.) as a business continuity plan (BCP) measure to provide temporary shelter for people who are unable to return home.
Group company property

- Upgrading air conditioning systems
- Concurrently with the renovation of offices at a Group company property, we upgraded the air conditioning system, which used a gas absorption chiller/heater generator as a heat source, to a multi-packaged air conditioner system designed for buildings with lower CO₂ emissions.
With the new system, we were able to reduce annual CO₂ emissions from the air conditioning system at the Group company property by 54% (-72 t-CO₂/year), while increasing thermal capacity by approximately 1.4 times compared to the conventional system.
Eco Ice

This system, which uses discounted nighttime electricity to store ice in thermal storage tanks, has been installed at three locations within the Isehara Works. The ice created during the night is used for cooling during the daytime, contributing to reduced building power usage and daytime peak power consumption.
In 2010, AMADA received the Heat Pump & Thermal Storage Utilization Award at the 13th Annual Thermal Storage Gathering in recognition of its ongoing efforts.
Disaster Prevention Energy Center

The Disaster Prevention Energy Center, a new facility that plays a central role in the AMADA Group’s BCP measures, was completed in September 2017.
In preparation for business continuity in the event of an emergency, this facility serves as the central hub for communication servers and electric power facilities, and is also equipped with an evacuation facility where 600 employees and residents of the surrounding area can subsist for three days. In addition, we have significantly improved the center’s seismic performance so that it can withstand an earthquake with a seismic intensity of 6 upper or more, and have made it possible for the electricity, drinking water, and heat that are essential for continuing business to be supplied to each building.

- Solar power generation
- The rooftop is equipped with a solar power generation system. The system consists of 144 solar panels, capable of generating up to 33 kWh in total. This can provide the power used in the Disaster Prevention Energy Center during the daytime.

- Micro-cogeneration generators
- The facility is equipped with eight 35 kW micro-cogeneration generators, which generate electricity within the Isehara Works and use the exhaust heat for air conditioning. This facility is responsible for supplying power within the site in case of a disaster.

- BCP-conscious water supply and drainage system
- Under normal conditions, the well water filtration equipment produces drinking water. In the event of an emergency, the system operates on emergency power and supplies drinking water to the Disaster Prevention Energy Center and the head office building, among other facilities. In a disaster, toilet drainage can be stored in the emergency drainage tank located in the underground pit, allowing 600 people to use the toilets for three days.
Fujinomiya Works

- NAS batteries
- Sodium–sulfur (NAS) battery facilities are systems for storing electric power at night and utilizing the batteries for electric power during the day. NAS batteries are subject to the Electric Power Load Smoothing Measures Promotion Policy enforced by the Japanese government.

- Thermal storage system (turbo chiller)
- During the night, electrical power is used to drive a turbo chiller and store cold water in a storage tank. The cold water is then used for production during the day.
AMADA received a certificate of appreciation from the Heat Pump & Thermal Storage Technology Center of Japan for the significant contributions made to CO₂ emission reductions by our large 1,000 ㎥ scale thermal storage system, which includes equipment for storing cold water at night.
Ono Plant

The Ono Plant was one of the first in the AMADA Group to implement energy-saving thermal electric equipment for air conditioning and to introduce renewable energy.
Toki Works

The Toki Works was one of the first in the AMADA Group to implement energy-saving measures. The energy consumed at the Technical Center is covered by solar power generation and other natural energy sources (energy creation), and together with the effects of energy conservation efforts such as the use of all LED lighting, we have achieved zero carbon emissions.
For these efforts, we received the 27th Promotion Award for Technology Promotion from The Society of Heating, Air-Conditioning and Sanitary Engineers of Japan.

- Solar power generation
- Solar panels installed on the roofs of the Technical Center building and the factory building create electricity. The total power output is approximately 300 kW.
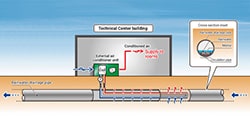
- Geothermal system
- Circulation pipes are installed in the rainwater drainage pipes on the premises to utilize geothermal energy, which maintains a constant temperature throughout the year, for heat exchange in air conditioners.
- Click on the image to enlarge
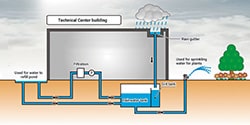
- Rainwater utilization system
- Rainwater falling on the roof is collected and used to replenish the pond and for plant irrigation.
- Click on the image to enlarge
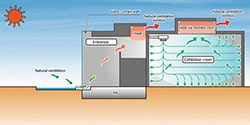
- Natural ventilation system
- The entrance is naturally ventilated using the chimney effect in the atrium. By keeping the exhibition hall pressurized, heat is dissipated from natural ventilation windows.
- Click on the image to enlarge
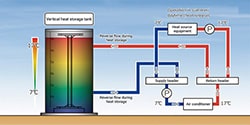
- Heat storage tanks
- Vertical heat storage tanks are used to accumulate cold and hot water at night when electricity is cheaper, which is then used for air conditioning in the factory during the day.
- Click on the image to enlarge
- Reducing power consumption with lower assembly man-hours
- The Toki Assembly and Manufacturing Department of the Toki Works is implementing initiatives to limit power consumption and reduce CO₂ emissions by reducing the number of assembly man-hours. In the manufacturing process for the ASFH3015G, a laser system peripheral device, a jig is fabricated and used to enable rail positioning with a single touch, saving 0.5 man-hours per unit. In addition, 172 other assembly improvements were implemented to reduce CO₂ emissions.
Isehara Suzukawa Works (AMADA PRESS SYSTEM)

- Solar power facilities for energy creation
- The Isehara Suzuki Works, which is a manufacturing base for stamping press equipment, was expanded and renovated in May 2024.
The S2 factory has been equipped with 90kW solar panels, generating 96MWh of electricity per year (41.6% of the works's current electricity consumption), reducing CO2 emissions by 37 tons per year and starting environmentally friendly factory operations.
Fukushima Plant (AMADA AUTOMATION SYSTEMS)

- Module MARS production system
- In conventional peripheral device production at the Fukushima Plant, in order to cope with customer needs (quick delivery, customized specifications, delivery month), the production load was at times low and at times overwhelming. This resulted in wasted materials, wasted energy, wasted man-hours, and excessive overtime. Considering our customers’ needs, we installed the automated material storage system (MARS), building a module production system to equalize the production load and to shorten lead time (reduction of man-hours, just-in-time).
AMADA Solution Center in Haan, Germany


- Use of geothermal energy
- The use of geothermal heat pumps covers about 80% of the energy required for annual heating and cooling, reducing CO₂ emissions by 40% compared to conventional systems.
Air conditioning efficiency is improved by installing air conditioning blowing ducts in the floor.
Amada Automation Europe headquarters and factory

At Amada Automation Europe, a manufacturing base for automation equipment in Europe, we are actively working toward carbon neutrality within Scope 1 and 2 of the Greenhouse Gas Protocol.
Electricity, which accounted for 75% of our CO₂ emissions in fiscal 2019, was entirely switched to renewable energy in fiscal 2023.
Various other energy initiatives were also implemented, including the use of biogas and waste heat. As a result, CO₂ emissions have been reduced by 94% from the 400 t-CO₂ of fiscal 2019.
We have achieved carbon neutrality by implementing further measures for our remaining CO₂ emissions, thus becoming the first manufacturing base in the Amada Group to reach this goal.

- Biogas introduced to new painting line
- Since the fall of 2023, we have also been using biogas to heat the new painting line’s ovens. At the same time we also installed a heat recovery pump that recycles the oven’s excess heat back into our water-based heating system.

- Painting ovens
- The painting ovens are equipped with biogas burners.

- Residual heat recovery system
- As part of our expansion, we also installed a heat recovery system that channels the compressor’s residual heat back into the factory’s heating system.
Product transportation and packaging
Adoption of blade tip guards made of biomass material

The Ono Plant has adopted biomass caps for some of the guards used to protect the band saw blade tips. Blending biomass made from rice bran and reducing the amount of polyethylene used has reduced CO₂ emissions from manufacturing, forming, and incineration by 16.5%.
