Ecological Facilities in Japan
Here are our ecological facilities in Japan :
Isehara Works
Amada Global Innovation Center
In February 2023, we opened a new base for innovations, the Amada Global Innovation Center (AGIC), by completely renovating the existing "Solution Center".
With the installation of the latest air conditioning equipment and lighting fixtures to save energy and the use of renewable energy generated by solar power systems, CO2 emissions will be reduced by 700 tons per year compared to the previous level.

Air Conditioning System with Electric Air-cooled Heat Pump Chillers
We replaced the existing gas absorption chiller/heater system with a high-efficiency modular electric air-cooled heat pump chiller system (*low GWP modular chiller). By switching to this new system, which uses electricity instead of gas, is designed with a large temperature differential system with a small flow rate, and uses an inverter variable flow pump to match the load, CO2 emissions will be reduced by 60% (-126 t-CO2/year) compared to the previous system.
*Adoption of R32, which has a lower global warming potential (GWP) than the conventional refrigerant R410A by approximately 68%. Thus, the impact on global warming will be significantly reduced.

Generating Energy by Solar Power System
By installing 255 kW solar panels to generate 220 MWh/year (10% of existing electricity consumption), CO2 emissions will be reduced by 100 tons/year.
Air Conditioning with Sensors for Exhibition Areas
The variable air volume air conditioning system using the PVAV (Powered Variable Air Volume) reduces fan power. This will reduce CO2 emissions by 20% compared to the level before the replacement. (-11 t-CO2/year)
By installing wireless thermostats in the areas with people and adjusting the amount of outside air based on the number of people counted by sensors, CO2 emissions will be reduced by 6% (-6 t-CO2/year) compared to the heat load in the exhibition room.
AMADA FORUM

Upgrading to Environmentally Friendly Equipment
In 2022, we upgraded the air conditioning system to a gas absorption chiller powered by waste heat, and installed a high-efficiency modular air-cooled electric heat pump chiller system (*low GWP modular chiller) and a VRF inverter system that can adjust to different loads.
We also installed a waste heat boiler to provide both air-conditioning (heating) and hot water supply.
Furthermore, we introduced the micro-cogeneration system*1 to reduce electricity demand and supply waste heat (hot water) to the hot/cold water generator and boiler, thus reducing their respective gas consumption.
These equipment upgrades will help us reduce our CO2 emissions by 40%. (-258 t-CO2/year)
We have also adopted R32 refrigerant, which has a lower global warming potential (GWP) than the conventional R410A refrigerant by approximately 68%, thereby significantly reducing the impact on global warming.
*1: In the event of a disaster (power outage), the micro-cogeneration system can be used to secure electric power (lights, outlets, network, ventilation, etc.) as a BCP measure to provide temporary shelter for people who are unable to return home.
Group company’s building

Upgrading of Air Conditioning System
Concurrently with the renovation of offices in our group company’s building, we upgraded the conventional air conditioning system using a gas absorption chiller/heater generator as the heat source to a multi-packaged air-conditioning system for buildings with lower CO2 emissions.
With the new system, we were able to reduce annual CO2 emissions from the air conditioning system of the group company building by 54% (-72 t-CO2/year), while increasing thermal capacity by approximately 1.4 times compared to the conventional system.
Eco Ice

This system, which uses discounted night-time electricity to store ice in storage tanks, has been installed at three locations within Isehara Works.
The ice created during the night is useful for cooling and contributes to reducing the building’s power usage and daytime peak power.
Disaster Prevention Energy Center
The Disaster Prevention Energy Center, a new facility that plays a central role in the AMADA Group's BCP measure, was completed in September 2017.
In preparation for continuing businesses in case of an emergency, this facility has gathered communication servers and power equipment and is equipped with an evacuation facility where 600 people, including employees and people in the surrounding area, can survive for three days. In addition, we have significantly improved the seismic performance so that it can withstand an earthquake with a seismic intensity of 6 or more, and electricity, drinking water, and heat that are essential for continuing business are supplied to each building.

Building overview
Scale :2 floors above ground
Structure :S structure (seismic isolation structure)
Building area :1,093.12 m2
Total floor area:1,430.50 m2
Height :9.9 m
Main features
Electric power and communication equipment
For the electric power and communication equipment, we have refurbished the head office infrastructure and installed a power supply and servers to supply electric power in order to ensure the safety of personnel and the electric power and information communication in case of an emergency.

Solar power generation
A solar power system is installed on the roof. The solar panel is composed of 144 sheets and can generate up to 33kWH. It can cover the power used in the Disaster Prevention Energy Center during the daytime.

Micro-cogeneration generators
The facility is equipped with 35kW x 8 micro-cogeneration generators, which not only generate electricity within the Isehara Works, but also use the exhaust heat for air conditioning. This facility supplies power to the works in case of a disaster.

Water supply/drainage system considering BCP
In normal times, the well water filtration equipment produces drinking water. In an emergency, the system operates with an emergency power supply and feed drinking water to the Disaster Prevention Energy Center, head office building, etc. Toilet drainage in case of a disaster can be stored in the emergency drainage tank in the underground pit, and 600 people can use the toilets for 3 days.
Fujinomiya Works
NAS battery

NAS (sodium/sulfur) battery facilities are systems for storing electric power at night and utilizing the batteries for electric power during the daytime. NAS batteries are subject to the Electric Power Load Smoothing Measures Promotion Policy prescribed by the Japanese government.
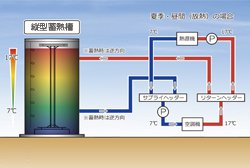
Storage heater system (turbo chiller)

Electrical power in the night is used to drive a turbo chiller and store cold water in a storage tank. The cold water is then used for production during the day.
AMADA received a certificate of appreciation from the Heat Pump and Thermal Storage Technology Center of Japan for the significant contributions made to CO2 emission reductions by our large 1,000m3 scale of our thermal storage system, which includes equipment for storing cold water at night.
Ono Plant
The heat pump chiller

The Ono plant upgraded their thermoelectric equipment for air-conditioning from “heavy oil absorption-type water cooler/ heater” to a “heat pump-chiller” in April, 2011.
As a result, we were able to cut CO2 emissions by 60% in the first half of FY2011, and 31% in the second half, or a 52% reduction for entire year.
Solar power generation

The entire lighting system in No.1 Plant is powered by solar panels installed on the plant’s roof at the time of its construction. They have a power output of 100 kW and produce 100,000 kWh of electricity a year, enough for about 300 households. An electronic noticeboard inside No.1 Plant displays current generating status, the amount of power gene- rated up to now and other information to employees.
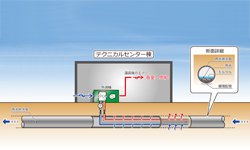
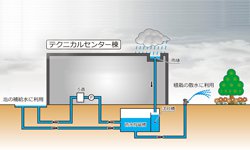
Toki Works
Various green devices at the Toki Office cover the energy used at the Technical Center.
LED Lighting

Faithful to its state-of-the-art and eco-friendly concept, Toki Works Technical Center is entirely lit by LED lighting. Great ingenuity has been applied to many aspects of the building where interior design was given high priority while dramatically reducing annual electricity consumption.
As a recognition of such achievements, AMADA Toki Works Technical Center won a prize for excellence in the Public and General Facilities category of the Ministry of the Environment's 2012 Power Saving and Lighting Design Awards.
Solar Power Generation

The solar panels on the roofs of the Technical Center and the factory generate electricity. Their output totals approximately 300 kW.
Fukushima Plant
Module MARS production system

In conventional peripheral device production at the Fukushima Plant, in order to cope with customer needs (quick delivery, customized specifications, delivery month), the production load was at times low and at times overwhelming. This resulted in wasted materials, wasted energy, wasted man-hours, and excessive overtime.
Considering our customers’ needs, we installed the Module MARS, building a module production system to equalize the production load and to shorten lead time (reduction of man-hours, JIT).
Full-scale operation began in FY2017, but electricity was reduced by 1.9% (55,300 kWh/25.9t-CO2), and LP gas by 10.9% (14.7 t/44.5t-CO2).
Looking forward, we will further promote the reduction of CO2 emissions through this Module MARS production system.
Contact for repair/recovery of AMADA products and our corporate activities.